Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms More
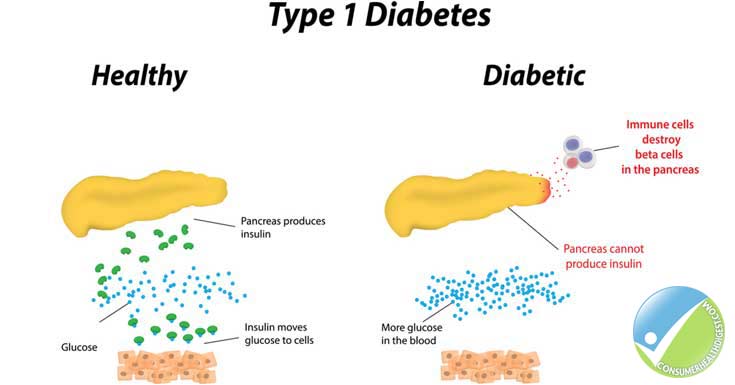
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to type 1 diabetes.
What is type 1 diabetes? type 1 diabetes is a condition in which your immune system destroys insulin -making cells in your pancreas. these are called beta cells. the condition is usually diagnosed. Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect major organs in your body, including heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. maintaining a normal blood sugar level can dramatically reduce the risk of many complications. eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. 1. heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases your risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, s Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to type 1 diabetes. although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults. despite active research, type 1 diabetes has no cure. treatment f Our patients tell us that the quality of their interactions, our attention to detail and the efficiency of their visits mean health care like they've never experienced. see the stories of satisfied mayo clinic patients.
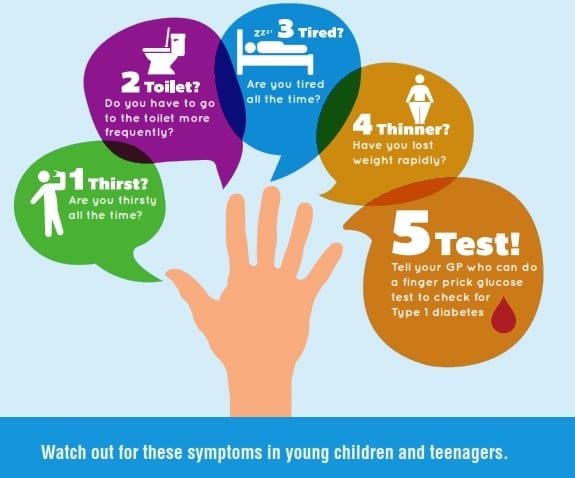
Type 1 diabetes signs and symptoms can appear relatively suddenly and may include: 1. increased thirst 2. frequent urination 3. bed-wetting in children who previously didn't wet the bed during the night 4. extreme hunger 5. unintended weight loss 6. irritability and other mood changes 7. fatigue and weakness 8. blurred vision. See full list on mayoclinic. org. There's no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes. but researchers are working on preventing the disease or further destruction of the islet cells in people who are newly diagnosed. ask your doctor if you might be eligible for one of these clinical trials, but carefully weigh the risks and benefits of any treatment available in a trial.
What Are Some Healthy Snack Ideas For Diabetics
What Is Diabetes Cdc
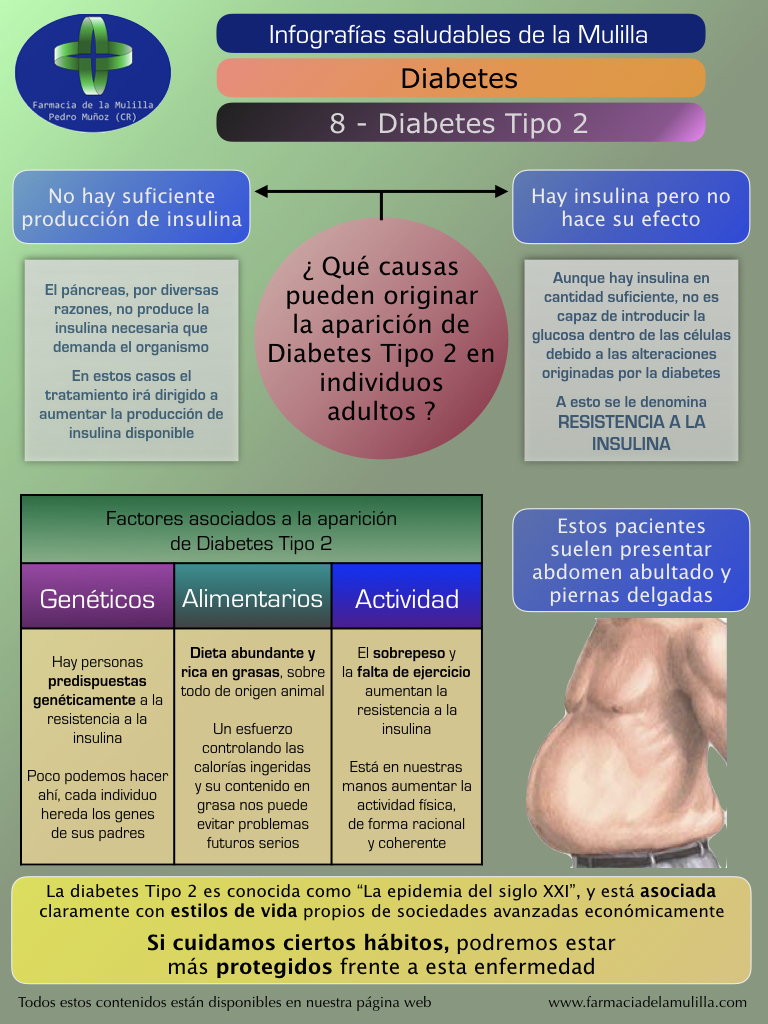
Type 2 diabetes: quick facts and the treatment you need.
It can take months or years for enough beta cells to be destroyed before symptoms of type 1 diabetes are noticed. type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. once symptoms appear, they can be severe. some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions. don’t guess—if you think you could have type 1 diabetes, see your doctor right away to get your blood sugar tested. untreated diabetes can lead to very serious—even fatal—health problems. risk Type 1 diabetes let’s fight type 1 diabetes together. with the right tools and support, you can do anything. whether you've been newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, are helping a loved one or have been managing your condition for a while, help is here. High blood sugar is damaging to the body and causes many of the symptoms and complications of diabetes. type 1 diabetes (previously called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes) is usually diagnosed in children, diabetes t 1 teens, and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
See full list on cdc. gov. Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar, or glucose. glucose is the fuel that feeds your body’s cells, but to enter your cells it needs a. See full list on cdc. gov.
Type 1 diabetes. type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that stops your body from making insulin. approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. symptoms of type 1 diabetes often develop quickly. it’s usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults. if. Type 1 diabetes was once often referred to as “juvenile diabetes”, but this is a misleading name as people of any age can develop type 1 diabetes. in fact, the prevalence of type 1 diabetes is increasing for all age groups across the world.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. this process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear. some people have certain genes (traits passed on from parent to child) that make them more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, though many won’t go on to have type 1 diabetes even if they have the genes. being exposed to a trigger in the environment, such as a More diabetes t1 images.
If your child has type 1 diabetes, you’ll be involved in diabetes care on a day-to-day basis, from serving healthy foods to giving insulin injections to watching for and treating hypoglycemia (low blood sugar; see below). you’ll also need to stay in close contact with your child’s health care team; they will help you understand the treatment plan and how to help your child stay healthy. much of the information that follows applies to children as well as adults, and you can also click diabetes t 1 here for The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. usually, the body's own immune system — which normally fights harmful bacteria and viruses — mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing (islet, or islets of langerhans) cells in the pancreas. other possible causes include: 1. genetics 2. exposure to viruses and other environmental factors.
What is diabetes? what causes diabetes? htq.
Some known risk factors for type 1 diabetes include: 1. family history. anyone with a parent or sibling with type 1 diabetes has a slightly increased risk of developing the condition. 2. genetics. the presence of certain genes indicates an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes. 3. geography. the incidence of type 1 diabetes tends to increase as you travel away from the equator. 4. age. although type 1 diabetes can appear at any age, it appears at two noticeable peaks. the first peak oc In the 1. 6 million people in the u. s. with type 1 diabetes, their insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells have been destroyed, meaning they can’t make insulin to process glucose diabetes t 1 into energy and.